These rules apply whether we're talking about a single Wi-Fi router, a mesh kit like Eero, Plume, or Orbi, or a set of wire-backhauled access points like Ubiquiti's UAP-AC line or TP-Link's EAPs. Unfortunately, these "rules" are necessarily closer to "guidelines" as there are a lot of variables it's impossible to fully account for from an armchair a few thousand miles away. But if you become familiar with these rules, you should at least walk away with a better practical understanding of what to expect—and not expect—from your Wi-Fi gear and how to get the most out of it.
Before we get started
Let's go over one bit of RF theory (radio-frequency) before we get started on our ten rules—some of them will make much better sense if you understand how RF signal strength is measured and how it attenuates over distance and through obstacles.
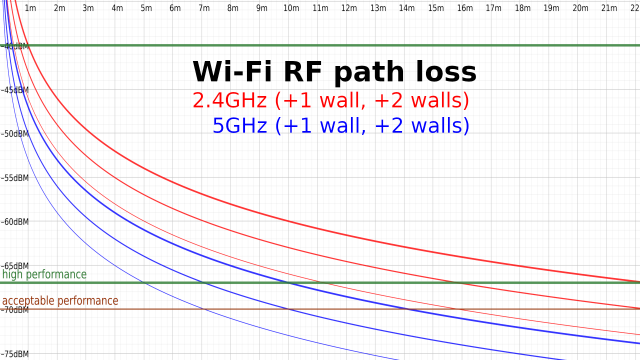
The above graph gives us some simple free space loss curves for Wi-Fi frequencies. The most important thing to understand here is what the units actually mean: dBM convert directly to milliwatts, but on a logarithmic base ten scale. For each 10dBM drop, the actual signal strength in milliwatts drops by a factor of ten. -10dBM is 0.1mW, -20dBM is 0.01mW, and so forth.
The logarithmic scale makes it possible to measure signal loss additively, rather than multiplicably. Each doubling of distance drops the signal by 6dBM, as we can clearly see when we look at the bold red 2.4GHz curve: at 1m distance, the signal is -40dBM; at 2m, it's -46dBM, and at 4m it's down to -52dBM.
Walls and other obstructions—including but not limited to human bodies, cabinets and furniture, and appliances—will attenuate the signal further. A good rule of thumb is -3dBM for each additional wall or other significant obstruction, which we'll talk more about later. You can see additional curves plotted above in finer lines for the same distances including one or two additional walls (or other obstacles).
While you should ideally have signal levels no lower than -67dBM, you shouldn't fret about trying to get them much higher than that—typically, there's no real performance difference between a blazing-hot -40dBM and a considerably-cooler -65dBM, as far away from one another on a chart as they may seem. There's a lot more going on with Wi-Fi than just raw signal strength; as long as you exceed that minimum, it doesn't really matter how much you exceed it by.
In fact, too hot of a signal can be as much of a problem as too cold—many a forum user has complained for pages about low speed test results, until finally some wise head asks "did you put your device right next to the access point? Move it a meter or two away, and try again." Sure enough, the "problem" resolves itself.
Rule 1: No more than two rooms and two walls
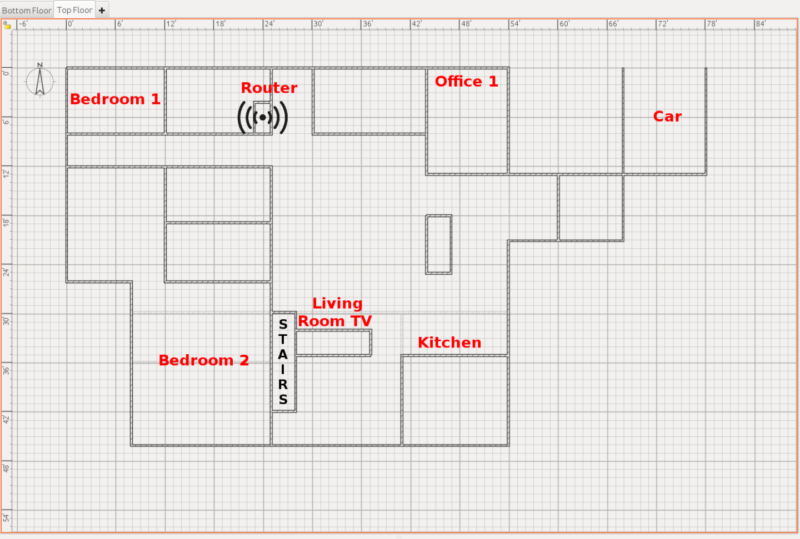
Our first rule for access point placement is no more than two rooms and two interior walls between access points and devices, if possible. This is a pretty fudge-y rule, because different rooms are shaped and sized differently, and different houses have different wall structures—but it's a good starting point, and it will serve you well in typically-sized houses and apartments with standard, reasonably modern sheet rock interior wall construction.
"Typically-sized," at least in most of the USA, means bedrooms about three or four meters per side and larger living areas up to five or six meters per side. If we take nine meters as the average linear distance covering "two rooms" in a straight line, and add in two interior walls at -3dBM apiece, our RF loss curve shows us that 2.4GHz signals are doing fantastic at -65dBM. 5GHz, not so much—if we need a full nine meters and two full walls, we're down to -72dBM at 5GHz. This is certainly enough to get a connection, but it's not great. In real life, a device at -72dBM on 5GHz will likely see around the same raw throughput as one at -65dBM on 2.4GHz—but the technically slower 2.4GHz connection will tend to be more reliable and exhibit consistently lower latency.
Of course, this all assumes that distance and attenuation are the only problems we face. Rural users—and suburban users with large yards—will likely have already noticed this difference and internalized the rule-of-thumb "2.4GHz is great, but man, 5GHz sucks." Urban users—or suburban folks in housing developments with postage-stamp yards—tend to have a different experience entirely, which we'll cover in Rule 2.
Listing image by Jim Salter

Rule 2: Too much transmit power is a bug
The great thing about 2.4GHz Wi-Fi is the long range and effective penetration. The bad thing about 2.4GHz Wi-Fi is... the long range and effective penetration.
If two Wi-Fi devices within "earshot" of one another transmit on the same frequency at the same time, they accomplish nothing: the devices they were transmitting to have no way of unscrambling the signal and figuring out which bits were meant for them. Contrary to popular belief, this has nothing to do with whether a device is on your network or not—Wi-Fi network name and even password have no bearing here.
In order to (mostly) avoid this problem, any Wi-Fi device has to listen before transmitting—and if any other device is currently transmitting on the same frequency range, yours has to shut up and wait for it to finish. This still doesn't entirely alleviate the problem; if two devices both decide to transmit simultaneously, they'll "collide"—and each has to pick a random amount of time to back off and wait before trying to transmit again. The device that picks the lower random number gets to go first—unless they both picked the same random number, or some other device notices the clean air and decides to transmit before either of them.
This is called "congestion," and for most modern Wi-Fi users, it's at least as big a problem as attenuation. The more devices you have, the more congested your network is. And if they're using the same Wi-Fi channel, the more devices your neighbors have, the more congested both of your networks are—each of your devices can still congest with one another, and still have to respect airtime rules.
If your own router or access points support it, turning your transmission strength down can actually improve performance and roaming significantly—especially if you've got a mesh kit or other multiple-AP setup. 5GHz typically doesn't need to be detuned this way, since that spectrum already attenuates pretty rapidly—but it can work wonders for 2.4GHz.
A final note for those tempted to try "long-range" access points: a long-range AP can certainly pump its own signal hotter than a typical AP, and blast that signal a greater distance. But what it can't do is make your phone or laptop boost its signal to match. With this kind of imbalanced connection scenario, individual pieces of a website might load rapidly—but the whole experience feels "glitchy," because your phone or laptop struggles to upload the tens or hundreds of individual HTTP/S requests necessary to load each single webpage in the first place.
Rule 3: Use spectrum wisely
In Rule 2, we covered the fact that any device on the same channel competes with your devices for airtime, whether on your network or not. Most people won't have good enough relationships with their neighbors to convince them to turn their transmission strength down—if their router even supports that feature—but you can, hopefully, figure out what channels neighboring networks use and avoid them.
This is usually not going to be an issue with 5GHz, but for 2.4GHz it can be a pretty big deal. For that reason, we recommend that most people avoid 2.4GHz as much as possible. Where you can't avoid it, though, use an app like inSSIDer to take a look at your RF environment every now and then, and try to avoid re-using the busiest spectrum as seen in your house.
This is, unfortunately, trickier than it looks—it doesn't necessarily matter how many SSIDs you can see on a given channel; what matters is how much actual airtime is in use, and you can't get that from either SSID count or raw signal strength in the visible SSIDs. InSSIDer lets you go a step further, and look at the actual airtime utilization on each channel.
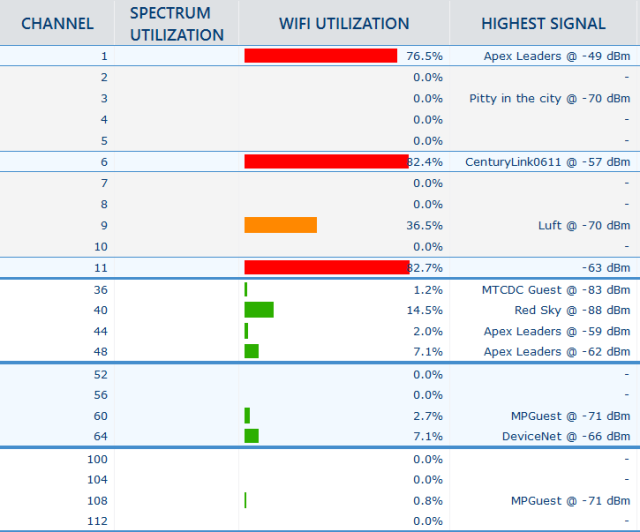
In the above inSSIDer chart, the whole 2.4GHz spectrum is pretty much useless. Don't get excited by those "empty" channels 2-5 and 7-10, by the way: 2.4GHz Wi-Fi gear defaults to 20MHz bandwidth, which means a network actually uses five channels (20MHz plus a half-channel margin on each side), not one. Networks on "Channel 1" actually extend from a hypothetical "Channel negative two" to Channel 3. Networks on Channel 6 really extend from Channel 4 through Channel 8, and networks set to Channel 11 actually occupy Channel 9 through Channel 13.
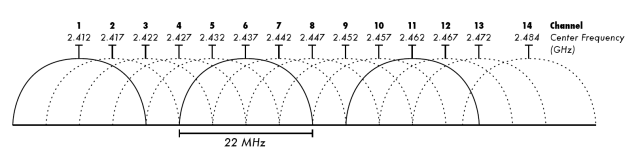
Congestion is a much smaller issue with 5GHz networks, because the much lower range and penetration means fewer devices to congest with. You'll frequently hear claims that there are also more 5GHz channels to work with, but in practice that bit isn't really true unless you're engineering Wi-Fi for an enterprise campus with no competing networks. Residential 5GHz Wi-Fi routers and access points are generally configured for either 40MHz or 80MHz bandwidth, which means there are effectively only two non-overlapping channels: the low band, consisting of 5MHz channels 36-64, and the high band, consisting of 5MHz channels 149-165.
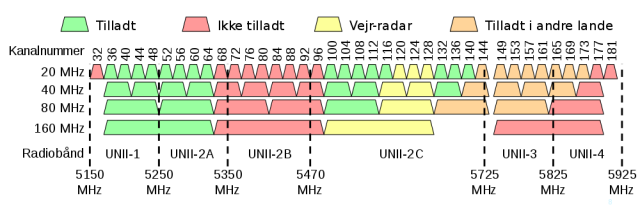
We fully expect to see a bunch of contention over this in the comments: technically, you can fit four 40MHz wide networks or two 80MHz wide networks on the lower 5GHz band. Practically, consumer gear tends to be extremely sloppy about using overlapping channels (eg, an 80MHz channel centered on 48 or 52), making it difficult or impossible to actually pull off that degree of efficient spectrum use in realistic residential settings.
There are also DFS (Dynamic Frequency Spectrum) channels in between the two standard US consumer bands, but those must be shared with devices such as commercial and military radar systems. Many consumer devices refuse to even attempt to use DFS channels. Even if you have a router or access point willing to use DFS spectrum, it must adhere to stringent requirements to avoid interfering with any detected radar systems. Users "in the middle of nowhere" may be able to use DFS frequencies to great effect—but those users are less likely to have congestion problems in the first place.
If you live near an airport, military base, or coastal docking facility, DFS spectrum is likely not going to be a good fit for you—and if you live outside the US, your exact spectrum availability (both DFS and non-DFS) will be somewhat different than what's pictured here, depending on your local government's regulations.
Rule 4: Central placement is best
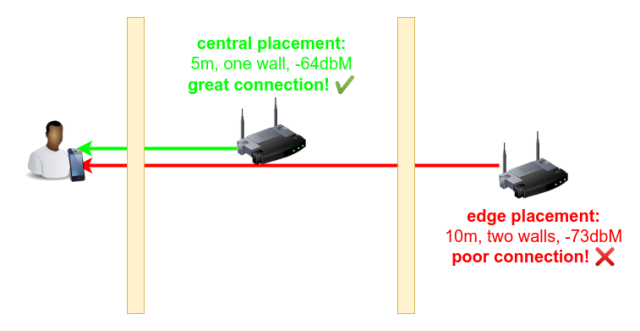
Moving back to the "attenuation" side of things, the ideal place to put any Wi-Fi access point is in the center of the space it needs to cover. If you've got a living space that's 30 meters end-to-end, a router in the middle only needs to cover 15m on each side, whereas one on the far end (where ISP installers like to drop the coax or DSL line) would need to cover the full 30m.
This also applies in smaller spaces with more access points. Remember, Wi-Fi signals attenuate fast. Six meters—the full distance across a single, reasonably large living room—can be enough to attenuate a 5GHz signal below the optimal level, if you include a couple of obstacles such as furniture or human bodies along the way. Which leads us into our next rule...
Rule 5: Above head height, please
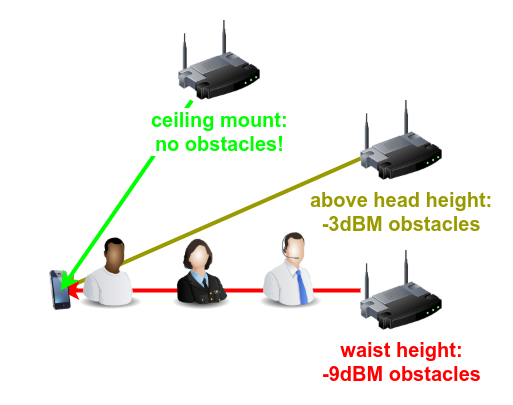
The higher you can mount your access points, the better. A single human body provides roughly as much signall attenuation as an interior wall—which is part of the reason you might notice Wi-Fi at your house getting frustratingly slower or flakier than usual when many friends are over for a party.
Mounting access points—or a single router—above head height means you can avoid the need to transmit through all those pesky, signal-attenuating meat sacks. It also avoids most large furniture and appliances such as couches, tables, stoves, and bookcases.
The absolute ideal mounting is in the dead center of the room, on the ceiling. But if you can't manage that, don't worry—on top of a tall bookshelf is nearly as good, particularly if you expect the access point in question to service both the room it's in, and the room on the other side of the wall its bookshelf or cabinet is placed against.
Rule 6: Cut distances in halves
Let's say you've got some devices that are too far away from the nearest access point to get a good connection. You're lucky enough to have purchased an expandable system—or you're setting up a new multiple-access point mesh kit, and still have one left—so where do you put it?
We've seen people dither over this, and wonder if they should put an extra access point closer to the first access point (which it has to get data from) or closer to the farthest devices (which it has to get data to). The answer, generally, is neither: you put the new AP dead in the middle between its nearest upstream AP, and the farthest clients you expect it to service.
The key here is that you're trying to conserve airtime, by having the best possible connection both between your far-away devices and the new AP, and between the new AP and the closest one to it upstream. Typically, you don't want to favor either side. However, don't forget Rule 1: two rooms, two walls. If you can't split the difference evenly between the farthest clients and the upstream AP without violating Rule 1, then just place it as far away as Rule 1 allows.
If this all seems too logical and straightforward, don't worry, there's another irritating "unless-if" to consider: some higher-end mesh kits, such as Netgear's Orbi RBK-50/RBK-53 or Plume's Superpods, have an extremely high-bandwidth 4x4 backhaul connection. Because this connection is much faster than the 2x2 or 3x3 connections client devices can utilize, it might be worth settling for lower signal quality between these units, with a degraded throughput that's still close to the best your client devices can manage.
If your mesh kit offers these very fast backhaul connections, and you absolutely cannot introduce any more APs to the mix, you might actually end up better off putting your last AP closer to the clients than to its upstream. But you'll need to experiment, and pay attention to your results.
Wi-Fi is fun, isn't it?
Rule 7: Route around obstacles

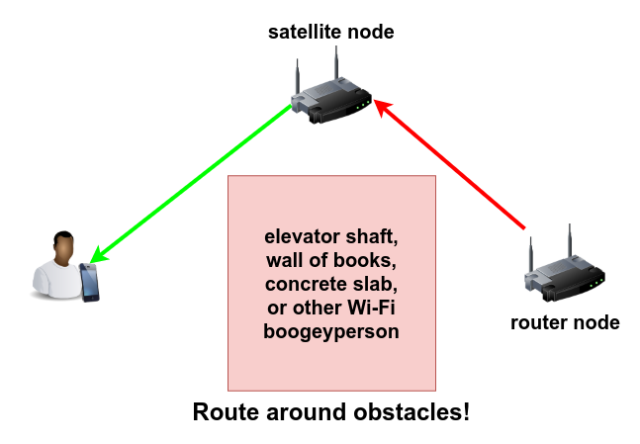
If you've got a really pesky space to work with, there may be areas that you just plain can't penetrate directly. For example, our test house has a concrete slab and several feet of packed earth obstructing the line-of-sight between the router closet and the downstairs floor. We've seen small businesses similarly frustrated at the inability to get Wi-Fi in the front of the office when the back was fine—which turned out to be due to a bookshelf full of engineering tomes lining a hallway, resulting in several linear meters of tightly-packed pulped wood attenuating the signal.
In each of these cases, the answer is to route around the obstruction with multiple access points. If you've got a Wi-Fi mesh kit, use it to your advantage to bounce signals around obstructions: get a clear line of sight to one side of your obstacle, and place an access point there which can relay from another angle that reaches behind the obstacle without needing to go directly through it.
With enough APs and careful enough placement, this may even tame early-1900s construction chickenwire-and-lath walls—we've seen people successfully place access points with clear lines of sight to one another through doorways and down halls, when penetrating the walls themselves is a job better suited to a hammer-drill than a Wi-Fi device.
If you've got too many obstacles to successfully route around, over, or under... see rule eight.
Rule 8: It's all about the backhaul
Most consumers choose pure Wi-Fi mesh, because it's convenient: you don't have to run any wires, you just plug in a bunch of access points and let them work out the magic between them, no fuss, no muss.
As convenient as this sounds, it's pretty much a worst-of-breed solution. Remember how we talked about congestion in Rules 2 and 3? It's still a problem here. If your client device has to talk to one access point which then has to relay that data to another access point, you're now using slightly more than double the airtime.
Now, this isn't really fair—you're using double the airtime if your client device was sitting where the satellite access point is; and since you followed Rule 6—cut distances in halves—that actually means the access point's connection upstream and to the client are much higher quality than the one the client would make directly to the upstream. So even in the absolute worst-case scenario—an access point which has to talk to its client on the same channel it talks to its upstream—this two-way relay can result in less airtime consumption than the client making one, much longer-range, lower-quality connection directly upstream.
However, it's much, much better to avoid the problem by talking downstream and upstream on separate bands entirely. Dual-band access points can do this by connecting to clients on the 2.4GHz radio, and the upstream (backhaul) connection on the 5GHz radio, or vice versa. In the real world, stubborn client devices (and stubborn users) frequently want to connect in sub-optimal ways, and you end up with clients on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz, so there's no one "clean" channel to backhaul on.
Really smart kits like Eero can work around that by dynamically routing backhaul, minimizing congestion by transmitting on different bands than they are receiving on, even when those bands change. More powerful tri-band kits like Orbi RBK-50/53 or Plume Superpods can avoid the problem by the use of a second 5GHz radio; this allows them to connect to clients on either 2.4GHz or 5GHz, while still having a clean 5GHz backhaul. (In Orbi, the backhaul radio is fixed and dedicated; Plume makes allocation decisions according to what its cloud optimizer decides is the best way to use airtime in that particular environment.)
The best answer, though, is not to use Wi-Fi backhaul at all. If you can run Ethernet cable, you should—not only is it faster than Wi-Fi, it doesn't suffer from Wi-Fi's congestion problems. Under heavy network load, cheap wired access points like Ubiquiti UAP-AC-Lites or TP-Link EAP-225v3s absolutely smoke even the best mesh kits, if the mesh kits are limited to Wi-Fi backhaul only. Wired backhaul can also conveniently overcome RF-opaque obstacles—if you can't punch a signal through it or relay around it, running a cable through it works wonders!
For users who aren't having much luck with mesh Wi-Fi and can't run Ethernet cables, modern powerline gear is also worth a look. Results absolutely vary depending on the quality of the house wiring and even the types of appliances connected, but in most cases, good AV2 (AV1000 or higher) or g.hn powerline gear is extremely reliable, with low latency nearly on par with Ethernet. The actual throughput is sharply limited—realistically, expect no more than 40-80Mbps for most real-world, across-the-house links—but if your killer app is gaming, or just web browsing that feels snappy, powerline can be a much better bet than Wi-Fi.
If you do go the powerline route, though, make certain you read the manual, and take the necessary steps to encrypt your connection. The first time we tested powerline gear, we accidentally bridged our powerline adapters with a neighbor's, and reconfigured his router—which was a similar model to the one on our test network, and had a default password—before realizing our error. "Hi, I hacked your router, sorry about that" is a crappy way to introduce yourself; we don't recommend it.
Rule 9: It's (usually) not about throughput, it's about latency
The great thing about throughput is, it's one great big shiny number that you can get in really easy ways—either by connecting to a speed test site like DSLreports, or by using a tool like iperf3 to connect to a local server.
The crappy thing about throughput is, it's a terrible way to measure either user experience, or the way a Wi-Fi network performs when actually under real load. Most people become unhappy with their Wi-Fi either when web browsing, or when gaming—not when downloading a big file. In both cases, the problem isn't "how many megabits per second can this pipe handle"—it's "how many milliseconds does it take for this action to complete."
Although it's possible to see a busy network's performance degrading by looking at "speed" numbers falling all around the network, it's a lot more confusing, complicated—and unrelated to the real world—than looking at application latency, which is a function of both raw speed and how efficiently the network manages its traffic and airtime.
When we test Wi-Fi networks, our killer metric is application latency, as measured by how long it takes to load a simulated, fairly complex web page. More importantly, it's how long it takes to load those web pages with lots of other things going on at the same time. Remember how we covered congestion in Rules 2 and 3—a "really fast" network with a single device active can turn into a bog-slow nightmare with many devices active—or, in many cases, with even one really poorly-connected device is active, which leads us nicely into our final rule.
The corollary to Rule 9 is, the AC speed rating is garbage—you should trust thorough, technically competent reviews far more than you trust a manufacturer's AC speed rating on a box.
Rule 10: Your Wi-Fi network is only as fast as its slowest connected device
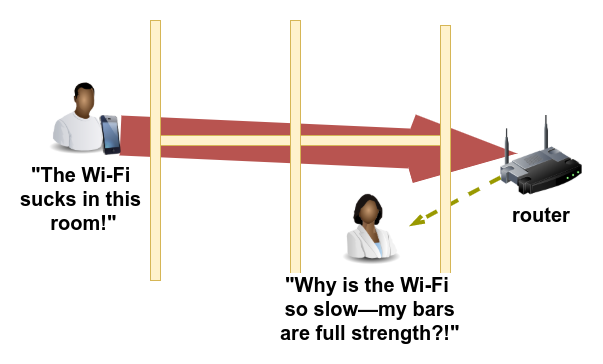
Unfortunately, one person struggling to watch a YouTube video in "that one bedroom with the crappy Wi-Fi" isn't just having a bad experience themselves—their bad time is bringing everybody down. All by itself, a phone in the same room with its associated access point might only need 2.5 percent of the available airtime to stream a 1080P YouTube video at 5Mbps. But a phone in "the bad bedroom," struggling with buffering and slowdowns, can consume 100 percent of the network's airtime trying—and failing!—to watch the same video.
Of course, streaming is very download-intensive, and routers or access points will typically refuse to transmit 100 percent of the time. An AP with lots of data to send will generally leave a little bit of airtime available for other devices to "speak up" and request their own data, after which it splits up download airtime between the nearby device and "the bad bedroom" in order to try to fulfill both their requests. However, that still adds tens or hundreds of milliseconds to the time it takes those other devices to wait for the access point to leave them a window, though—and they still have to compete with one another when such a window opens.
It gets even worse if the user in "the bad bedroom" tries to upload a video, send an email, or post a big photo to social media. The router tries to leave some airtime open for other devices to speak up—but the user's phone is under no such restraints, and it will cheerfully eat up every bit of airtime it can. Worse, the phone has no idea how much data other users may have requested, in any brief windows they had to make requests. The router knows how much data needs to be delivered to each client individually, so it can allocate airtime for downloading data appropriately—but all the phone knows is it wants to get this stuff uploaded, so everybody's experience is awful while it does it. So if you leave all this wisdom behind with just one rule in mind, this should probably be it.
https://news.google.com/__i/rss/rd/articles/CBMib2h0dHBzOi8vYXJzdGVjaG5pY2EuY29tL2dhZGdldHMvMjAyMC8wMi90aGUtYXJzLXRlY2huaWNhLXNlbWktc2NpZW50aWZpYy1ndWlkZS10by13aS1maS1hY2Nlc3MtcG9pbnQtcGxhY2VtZW50L9IBAA?oc=5
2020-02-23 14:30:00Z
CBMib2h0dHBzOi8vYXJzdGVjaG5pY2EuY29tL2dhZGdldHMvMjAyMC8wMi90aGUtYXJzLXRlY2huaWNhLXNlbWktc2NpZW50aWZpYy1ndWlkZS10by13aS1maS1hY2Nlc3MtcG9pbnQtcGxhY2VtZW50L9IBAA
Bagikan Berita Ini














0 Response to "Ten rules for dating my teenage daughter placing your Wi-Fi access points - Ars Technica"
Post a Comment